|
|
THE NATIONAL AIDS AUTHORITY
Achievement 1998-2003 and Priorities needs for 2004-2006
|
By the use of the Asian
Epidemic Model (AEM) and based on the results of 8 rounds of HIV/AIDS
Sentinel Surveillance and 6 Rounds of Behavioral Sentinel Surveillance,
the Ministry of Health estimates the that there is a reduction of the
Number of people currently living with HIV/AIDS from 175,000 in 1998 to
157,500 in 2003.

Number of people
currently living with HIV/AIDS
This means that the
prevalence of HIV infection on 15 to 49 years old people has dropped from
3.3% in 1997 to 2.6% in 2003. This clearly demonstrates that the joint
efforts of the Royal Government of Cambodia, legislative branch, Civil
Society, local authority , private sector and especially the participation
of PLWAs enables Cambodia to become one of the five successful countries
in the world in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
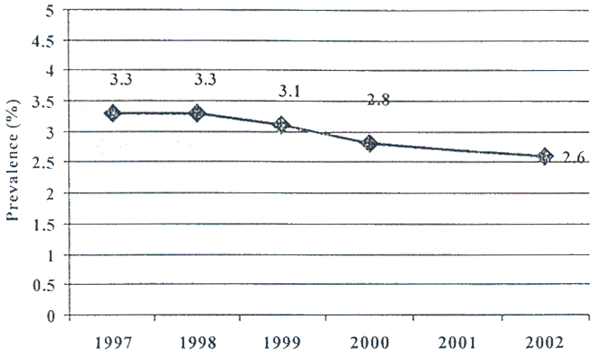
Prevalence of HIV
infection on 15 to 49 years old
On the other hand, this
model estimates that the Cumulative AIDS Death had in crease from 30,300
in 1998 to 78,700 in 2002. Moreover, it is known that Cambodia is unevenly
attacked by HIV/AIDS epidemic where the west of the country is much more
affected by comparison to the central and east parts.
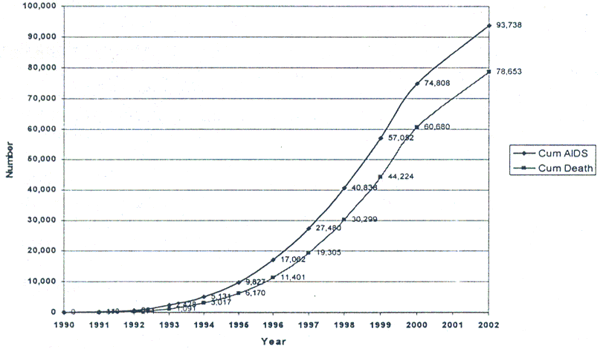
Cumulative AIDS Death
There are a number of
concerns that need to be brought into consideration
-
HIV/AIDS
epidemic is generalized and reaching rural and urban area alike.
-
In contrast
to High risk Behavior Groups, there is no drop in incidence on
housewives and babies. In 2002, 42% of new infection occur through the
transmission from husbands to wives. Peri-natal transmission is then
ranked as the second highest route of transmission.
-
On the other
hand , there are emerging there are new groups with increasing risk
behavior such as Garment Factories Workers , Migrants (internal and
cross border) , young people (in and out of schools) drug users, MSM
(Men have sex with Men)
-
The burden
for Care and Support are increasing with accumulation of new HIV
infected and AIDS patients to the current PLWAs. Access to care and
treatment services is another concern partly because of the costly drugs
both for Opportunistic infection treatment and Antiretroviral Therapy.
-
Up to the
year 2002, the Ministry of Health estimated that there are around 94,000
deaths due to AIDS leaving behind almost 100,000 children and old people
without support (Source AEM). This pauses a serious need for impact
mitigation that should go along with prevention, care and support
efforts.
Overall achievement
-
Owing to the
Ministry of Health’s estimates, it was found that the combined effort
for about 10 years (from 1991-2002) of government institutions, civil
society, local authority along with technical and funding support from
United Nations agencies and donors help us to prevent 700,000 people
from being HIV infected, almost 100,000 people had undergone Testing and
counseling services, 2000 AIDS patients had access to ARVs, and 100
Million condom was sold. During 1998-2003 74 Millions USD (mostly from
UNs and donors) have mobilized to the response to HIV/AIDS. Around 80
NGOs have been working on HIV/AIDS.
Laws, Policies and
Structure
-
In 2003, the
National Assembly passed the Law for Prevention and Control of HIV/AIDS
enabling an effective prevention and a better environment for the
quality of life of those infected and affected by HIV/ AIDS through
provision of care and welfare services.
-
Since
HIV/AIDS is considered as a National Priority it was integrated into the
Socio- Economic Development Plan II and The National Poverty Reduction
Strategy. (NPRS).
-
The creation
of the National AIDS Authority as a National body for coordinating and
facilitating comprehensive and multi-sectoral response to HIV/AIDS. This
mechanism comprises 26 Ministries and 24 Provinces and Municipalities
which had extended their respective vertical and horizontal network down
to district level.
-
In late 2003,
the National AIDS Authority- Coordinating Committee (NAA-CC) has been
created to coordinate with UN agencies, Donors and major NGOs through
regular monthly meeting.
-
Special
Coordinating body between GOs and NGOs has been created to orchestrate
campaigns during World AIDS Day, Water Festival and Candle light
Memorial.
Sectoral Policies
-
In 2002 The
Ministry of Cults and Religions passed the” Policy on Religious Response
to the HIV/AIDS Epidemic in Cambodia”
-
In 2003: The
Ministry of Women and Veteran Affairs passed the Policy on Women, the
Girl Child and STI/HIV/AIDS.
-
In 2003 with
support from donors (USDOL, WVC...), International Labor organization
and the Ministry of Ministry of Social Affairs Labor and Youth
Rehabilitation launched Code of Practices Regarding HIV/AIDS in the
Workplace.
Strategic Plan
Development
-
In 2001, the
NAA launched the National Strategic Plan for Comprehensive and Multi-sectoral
response to HIV/AIDS 2001-2005.
-
Subsequently,
five Ministries had developed their Strategic Plan for the response to
HIV/AIDS namely, Ministry of Health, Ministry of National Defense,
Ministry of Education Youth and Sport, Ministry of Social Affairs Labor
and Youth Rehabilitation and Ministry of Rural Development.
-
Besides
Battambang and Siam Reap Provinces had succeeded in developing their
Comprehensive and Multisectoral Plan for HIV/AIDS Response.
Program Interventions
Based on the
implementation of the National Strategic Plan for Comprehensive and
Multi-sectoral Response to HIV/AIDS, Cambodia had launched initiatives for
a changes in the development of our Prevention, Care and Support and
Mitigation of impact interventions both in the government institutions and
Civil Society
Prevention
-
The
implementation of country wide 100% Condom Use Program succeeds in
reducing HIV Prevalence among Direct Sex Workers from 51% in 1998 to
28.8% in 2001. However, this program is also covering indirect sex
workers as well.
-
With an
countrywide 100% Condom use Program addressing brothel based sex work,
unsafe sex with direct Sex Workers is remarkably reduced (Rate of
consistent condom of men visiting brothels is increased from 43% in 1997
to 87% in 2003).
-
Up to 2003,
Peer Education Program has been successfully covered 70% of the Military
forces and 25% of the Police force.
-
The two High
Patriarch Monks and the Ministry of Cult and Religion along with support
from donors land civil society manage to increase the participation of
monks, achars and nuns in HIV/AIDS response. Countrywide, around 50,000
Buddhist monks are integrating HIV/AIDS issues into moral preaching by
asking their disciples to adopt safer behavior.
-
Ministry of
Education Youth and Sport tries hard to give background information and
skills on HIV/AIDS aiming to protecting up to 20% of in school students
and 70% of teachers countrywide.
-
With the
support of Ministry of Social Action Labor Vocational Training and Youth
Rehabilitation a long with support from United Nations NGOs employers
and employees, HIV/AIDS interventions has been undertaken to 30 out of
200 Garment Factories country wide covering approximately 20%.
-
In Private
sector , efforts has been made to provide HIV/AIDS education to Beer
Girls, Hotels , casino staff, Caltex, Coca Cola staff, driving school
students.
-
Ministry of
Rural Development Community infrastructure such as Village Development
Committee, Village Health Volunteers and Youth volunteers in 6 provinces
to increase community response to HIV/AIDS in 1,000 villages.
-
Nowadays,
mobile population is attracting the concerns of government NGOs and
donors agencies. However, the coverage of the activities with this group
is still limited.
-
Besides
social marketing of condom leads to an incremental sale with 100 Million
condoms sold between 1994 and 2004. The annual sale in 2004 alone is
about 20 million.
Care and Support
-
For care and
support there is also a remarkable improvement. The expansion of
Voluntary and Confidential Testing services covers 13 provinces and
municipalities with 49 VCCT Centers where 18 are managed by NGOs. The
total number of people undergone HIV testing & Counseling from 1998 to
2003 is 90, 318. Up to 2003, 2000 out of 22,000 PLWAs have access to
free Anti Retroviral Therapy (ARV). In order to expand care and support
services, the Ministry of Health develops policies and strengthens its
structure to improve interventions. Friends Help Friends (Modul Mith
Chouy Mith MMM) and Home Based Care team have been expanded to
operational district and commune levels to encourage the use of services
at local level. On the other hand, the Ministry of Health encourages the
involvement of private practitioners to observe health care standard for
improving the quality of services. Moreover, there were efforts from
Blood safety, Tuberculosis, Maternal and Child Heath and Reproductive
health to contribute for a join response to HIV/AIDS.
-
Besides, the
right of People Living with HIV/AIDS (PLWAs) and those who are affected
by this epidemic. The Cambodian PLWAs Network ( CPN+) work with 1000
members of 24 groups in 10 Provinces to reach 4000 PLWAs in the country
to improve their involvement for the response to HIV/AIDS.
-
Nowadays, the
National AIDS Authority with the support from donors and Non
Governmental Organizations is developing the Guidelines for the
Implementation of HIV/AIDS Law leading to the training of Commune
Councils to reduce stigma and discrimination to PLWAs.
Mitigation of
impact
-
With the
support from WFP and through partnership with Ministry of Health and
NGOs (KHANA, WVC and Caritas), 4,000 households living in food insecure
areas had receive monthly food rations.
-
Some NGOs
such as NPC, BFD, PC, SCC, COERR, SCFA, TPO, Tear Fund, SHCH, Marknoll,
NYEMO, Caritas... provide some inputs for the mitigation of impact of
HIV/AIDS.
-
Beyond
prevention, care & Support and mitigation of impact, the National AIDS
Authority gained a strong support from UNDP to build the capacity for
deep response to HIV/AIDS though Leadership for Results Program where
200 participants (2 Groups) coming from different level and different
background joined 3 separate sessions On the other hand, 7 Provinces has
initiated Community Capacity Enhancement to empower community for a
sustainable response at local level.
International
Collaboration
Since Cambodia is a
developing country, HIV/AIDS Program of both the Government and the civil
society is collaborating with United Nations agencies and international
donors to mobilize the resources for the response to this epidemic:
|
Table 1-
FINANCIAL CONTRIBUTION TO NATIONAL RESPONSE ON HIV/AIDS |
|
(Contribution in
USD) |
|
|
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
National budget
(NCHADS) |
733,071 |
937,000 |
945,800 |
950,000 |
950,000 |
950,000 |
950,000 |
950,000 |
|
National budget
(NAA) |
|
|
|
378,454 |
|
|
|
|
|
World Bank
Credit |
1,093909 |
500,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXTERNAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADB Grant to
(NCHADS) |
45,540 |
711,645 |
723,244 |
1,215623 |
|
|
|
|
|
WB Grant to
(NCHADS) |
|
|
|
400,000 |
400,000 |
400,000 |
400,000 |
400,000 |
French
Cooperation
Grant |
76,000 |
544,000 |
544,000 |
200,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
DFID Grant to
NCHADS |
|
|
1,308800 |
1,566283 |
1,566283 |
1,566283 |
1,566283 |
82,130 |
DFID Grant to
NAA |
|
|
537,263 |
778,202 |
847,118 |
780,163 |
752,265 |
50,430 |
|
DFID Grant to MoEYS |
|
|
743,901 |
1,209038 |
1,219141 |
1,167719 |
1,195315 |
53,333 |
|
DFID Grant to BBC |
|
|
800,000 |
1,197000 |
1,197000 |
1,197000 |
1,197000 |
|
|
DFID Grant to PSI |
1,000000 |
1,300000 |
1,300000 |
1,500000 |
1,500000 |
|
|
|
|
EU-Grant through
ITM |
|
|
|
1,500000 |
1,500000 |
1,500000 |
0 |
0 |
|
Research
Consortiums (UNSW. etc.) |
|
|
100,000 |
600,000 |
600,000 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
USCDC-GAP Grant to
NCHADS, NIPH |
|
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
1,400000 |
|
USAID Grant to NGOs |
4,700000 |
6,200000 |
9,164388 |
10,000000 |
1,000000 |
1,000000 |
1,000000 |
1,000000 |
|
Other NGOs |
3,559925 |
3,714492 |
4,765000 |
4,500000 |
4,500000 |
4,500000 |
4,500000 |
4,500000 |
|
UNDP through NAA |
1,482050 |
400,000 |
129,565 |
746,985 |
896,750 |
3,000 |
|
|
|
EU/UNFPA |
900,000 |
760,000 |
147,069 |
1,328077 |
1,200251 |
|
|
|
|
UNFPA |
|
456,151 |
842,081 |
198,906 |
284,578 |
|
|
|
|
WHO |
256,300 |
|
172,843 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNICEF |
1,493000 |
1,434000 |
2,157000 |
1,970000 |
|
|
|
|
|
JICA |
70,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNAIDS |
80,000 |
|
366,340 |
192000 |
422000 |
|
|
|
|
GRATM (R1+R2+R4) |
0 |
0 |
8,208155 |
8,404947 |
3,249676 |
5,545308 |
7,855898 |
8,805807 |
|
TOTAL RESOURCES
AVAILABLE |
15,489795 |
18,357288 |
34,337449 |
40,235515 |
31,732797 |
29,009473 |
29,816761 |
26,241610 |
| 3-
Priorities areas for HIV/AIDS Response |
HIV/AIDS epidemic is an
emerging public health and development concern. The paradox is that it
requires effective attention at this early, less evident stage of the
epidemic, and of Cambodia’s transitions to modernity and development, if a
public health crisis is to be averted.
The vision of the Royal
Government of Cambodia for the country’s economic development and social
well-being is contained in its Rectangular Strategy. The
inter-connectedness of the HIV epidemic and development should be able to
be shown through this strategic framework as a guide for the priorities
areas selection for HIV/AIDS response in the next two years.
The first side of the
Rectangular strategy is building Peace, Political Stability, and Social
order for the nation and people.
The achievement of peace,
security and stability is directly related to the strength of civil
society and its organisations, to the emergence of moral leaders and
public intellectuals, and to the creation of social capital. Without each
of these, Cambodia will not be able to respond effectively to the HIV
epidemic.
The second side and third
side of the Rectangular strategy is “Cambodia’s integration into the
region and normalizations of relationships with the international
community” and building “Partnership in development”
Cambodia needs to ensure
that it negotiates and legislates WTO membership such as to take full
advantage of the TRIPS provisions that would enable it to access existing
HIV treatment drugs and new HIV treatment drugs and vaccines in the most
appropriate and equitable manner.
Cambodia’s integration
into the region will strengthen its ability to initiate and join in
inter-country and sub-regional responses to the shared problems of the HIV
epidemic. It will also facilitate Cambodia’s ability to enter into
effective public-private partnerships to improve accessibility, quality
and affordability of HIV drugs and technology.
The fourth side of the
Rectangular strategy is to promote “Favorable macroeconomic and financial
environment”
To enable capacity
building and human resource development, public administration reform has
to be decentralized and deconcentrated. HIV/AIDS epidemic requires the
principle of subsidiary: that responsibility for action be devolved as
close to communities as possible. It requires strong and functioning local
and regional government and civil society organizations. Local
coordination and collaboration mechanisms need to be supported and
financed. On the other hand planning should ensure the continuing capacity
to function of the public sector, especially of the health and education
sectors.
Methodology
Priorities areas for
HIV/AIDS response in Cambodia depends on the situation and response
analysis as gathered through passive and active data collection (both
quantitative and qualitative data).
For the purpose of this
Consultative paper preparation ,the National AIDS Authority had invited
relevant partners from the Technical Board ( Ministries including the
National Center for HIV/AIDS Dermatology and Sexually Transmitted
Infections (NCHADS ) of Ministry of Health ) , from selected NGO (such as FHI, Khana, PSI,CARE , WVC, HACC, RHAC...) and from United Nations and
Donors (UNAIDS UNDP,DFID, ILO , CDC - GAP) to two consultative meetings.
In these consultative
processes and based on available data (especially the HIV Sentinel
Surveillance (HSS), the Behavioral Sentinel Surveillance (BSS) and the
Asian Epidemic Model (AEM) developed by NCHADS in 2002) and the HIV/AIDS
response from different partners working both at central level and in the
fields, it was recommended that:
-
For
prevention:
-
Efforts
should be made to continue , to expand and to strengthen existing
preventive program targeting identified groups with high risk behavior
(such as Peer education with Military , Police , Garment factory
Workers, Students, Out of School Youth , Sex workers (both direct and
indirect), migrants, MSMs…
-
It is an
imperative to support interventions aiming to protect Housewives from
being infected by their husbands by innovative and decentralized
response down to family and community. This aims to empower people to be
responsible for themselves as well for their families.
-
With emerging
groups at increasing risks interpersonal intervention such as peer
education and media approach can enhance an appropriate social norm and
an enabling environment for safer practices and positive networking to
reduce the vulnerability to HIV/AIDS.
-
For care and
support: It is understood that the rational behind Care and support
efforts is to lower down the social and economic burden to the whole
country on a growing needs of HIV/ AIDS dependants (both children and
elderly) and to improve the quality of life of PLWAs enabling them to
continue/ to join their jobs and to have a peaceful living within family
and community. Efforts should support the Continuum of Care (COC)
Strategies of NCHADS/ Ministry of Health encompassing VCCT (Voluntary
Confidential Counseling and Testing), Treatment of Opportunistic
Infections, Anti-Retroviral Therapy, Treatment of co-infection HIV and
TB, Supporting Home based Care and Mondul Mith Chouy Mith (MMM) and the
Monitoring and evaluation of COC Program.
-
For the
mitigation of impact: Efforts should increase the coverage to address
the needs of Orphans and Vulnerable Children and those affected by
HIV/AIDS. Besides institutional care, poor PLWAs are lacking of
financial support for their regular follow up visit and at list one year
food subsidy to recover and to go back to their work.
Budget availability and
gap
-
For
Continuum of Care package:
Since there is a
calculation tools for estimating the need and availability of funding
for continuum of care ,it is known that:
-
for 2004,
there is no gap in funding.
-
for 2005,
$1,948,568 are requested to compliment the existing funding including
GFATM.
-
for 2006,
$1,918,606 are requested to compliment the existing funding including
GFATM.
-
for 2007,
$1,990,241 are requested to compliment the existing funding including
GFATM.
-
for 2008,
$1,952,989 are requested to compliment the existing funding including
GFATM.
Table 2- Continuum of Care funding: Availability, total
cost and Gap
|
|
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
|
Available funds |
$11,564,430 |
$12,446,079 |
$13,862,281 |
$14,589,378 |
$19,787,468 |
|
Total need/cost |
$11,564,430 |
$14,394,647 |
$15,780,887 |
$16,579,620 |
$21,740,457 |
|
Gap |
$0 |
$1,948,568 |
$1,918,606 |
$1,990,242 |
$1,952,989 |
-
Combined need for Prevention, Surveillance & Research, Coordination and
Institutional Strengthening and Impact mitigation
With the recommendations as listed above, there are needs to increase
different components:
-
Prevention:
Interventions for family and community at villages’ level is becoming
heavy due the large size of this target. Moreover, although existing
target groups (Military, Police Workers ...) may no longer need costly
intervention as compared to the starting point but groups with
increasing risks may require substantial funding support such as
migrants, Out of school Youth, Drug users... That is why is was
suggested to increase by 25% to the prevention budget in 2004 and
onwards.
-
Small
increase budget increase is made for Surveillance & Research and Impact
mitigation.
-
However, for
Coordination and Institutional Strengthening, there is a need to augment
support in order to decentralize response down to community level.
Table 3- The subtotal
cost for Prevention, Surveillance & Research,
Coordination and Institutional Strengthening and Impact mitigation
|
|
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
|
Available Fund |
28,671,085 |
19,286,718 |
15,147,192 |
15,227,383 |
6,454,142 |
|
Prevention, Surveillance & Research, coordination & Institutional
Strengthening, and Mitigation |
$10,575,504 |
$13,591,008 |
$16,988,760 |
$21,235,950 |
$26,544,938 |
|
|
$18,095,581 |
$5,695,710 |
- $ 1,841,568 |
- $ 6,008,567 |
- $ 20,090,796 |
Due to this estimate and
base on the total resource available (from table I and table 2) it was
found that:
-
in 2004, there
no funding gap.
-
in 2005 ,there
no funding gap
-
in 2006, about
1,841,568 USD are needed.
-
in 2007, about
6,008,567 USD are needed.
-
And in 2008,
about 20,090,796 USD are needed
2004 CG Benchmarks:
-
Expansion of
prevention programs to cover drug users, men who have sex with men,
factory workers and mobile populations, as well as prevention of Mother
to Child Transmission (PMCTC), and Voluntarily confidential Counseling
and Testing (VCT).
-
A revised and
approved National Strategic Plan (2006-2010) with a unified and
functioning Monitoring and Evaluation Framework in place by 2005. This
plan is implemented at provincial level by the end of 2006.
***************************** |







