|
Summary Progress Report of Joint Technical Working Groups Prepared for the 18th meeting of the Government-Development Partner Coordination Committee April 2011
I. Introduction This report is being prepared for the 18th meeting of the Government-Development Partner Coordination Committee (GDCC) to be held on 20 April 2011. It documents the implementation by Technical Working Groups (TWGs) of their planned activities for 2010 and 2011. It also presents a consolidated report on progress in implementing activities of the Joint Monitoring Indicators endorsed at the 3rd meeting of the Cambodia Development Cooperation Forum (3rd CDCF) in June 2010, including activities intended to increase aid effectiveness.
In preparing this report, the Cambodian Rehabilitation and Development Board of the Council for the Development of Cambodia (CRDB/CDC) as the secretariat of the GDCC made use of the reports on progress prepared and submitted by TWGs and the government agency (in this case the Anti-Corruption Unit). Almost all reports of progress were submitted to the GDCC secretariat by the indicated deadline 31 March 2011. CRDB/CDC would like to acknowledge this effort by all TWGs.
In the main reports from TWGs indicate that most of the activities planned by TWGs for 2010 were implemented. Though not the case for all TWGs, the results have been encouraging. By now, all TWGs have already prepared and endorsed work plans for 2011. Reporting by TWGs indicates the important role of Technical Working Groups as a forum for multi-stakeholder dialogue led by government ministries and agencies. Topics discussed by TWGs ranged from broader policy issues, to programming and design and operational issues involving different areas and at many levels, capacity development, and aid effectiveness such as tailoring programmatic approaches to the sector or mainstreaming results into policy implementation. TWGs have also been considered as a mechanism for regular information sharing and communication between stakeholders. Challenges, however, remain. As the reform programs of the government advance, new tasks and issues emerge that are wider in scope (involving different ministries and agencies) and complicated in nature and that cannot be just readily addressed under the mandate of any one ministry or agency. New actors have also participated. All of these require clear guidance for TWGs to operate and function and to ensure that the activities undertaken by TWGs are linked to national framework and contribute to broader development results. On the other hand, resources and the issues of capacity continue to be constraints for most TWGs. The revised Guideline on the Role and Functioning of TWGs (issued by the government in November 2010) attempts to provide guidance to TWGs on issues necessary for an effective and efficient functioning of TWGs including size and membership composition, addressing cross-cutting issues and support structures.
Progress in JMI implementation has been encouraging in many cases. Most activities in the JMI matrix endorsed at the third CDCF meeting in June 2010 are being implemented and TWGs are closely monitoring their progress. Although challenges remain, progress is expected to be realized for all the agreed targets of the JMIs within the existing timeframe of implementation, if the current effort can be sustained and challenges addressed.
This document is organized as follows: the next section provides an overview of the implementation of TWG work plans during 2010 and the emerging overall shape of the activities planned for 2011. Then the section that follows consolidates the progress reported by TWGs in implementing JMI activities and the last section reports on progress against the aid effectiveness priorities associated with each TWG and the challenges encountered. II. Implementation of planned activities by TWGs
1) The year 2010: progress and challenges
For Technical Working Groups, most activities
planned for 2010 have been implemented or are being implemented on schedule.
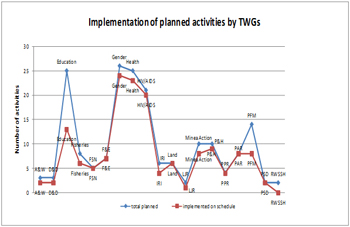
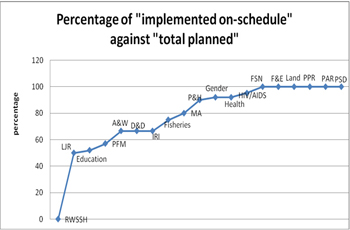
The charts below plots the number (and percentage) of activities implemented
"on schedule" against total number of activities planned by TWGs*. "Click on the image below to view full size" |
|
Common areas of activities include:
a)- Strategic policy discussion TWGs reported that a number of important policy issues were brought for discussion during the meetings of TWGs. They ranged from strategic dialogue with partners on key issues specific to sector (such as the role of NGO partners) to the development of strategies and policies for sectors or thematic areas. Chief among these are the monitoring of the formulation of the Education Strategic Plan 2009-2013 (Education TWG), the development of the National Forestry Program by the Forestry and Environment TWG, dissemination of the Neary Rattanak 3 including monitoring and resource mobilization for implementation (Gender TWG), strategic dialogue on the Health Strategic Plan 2 and the International Health Partnership (Health TWG), and the preparation of a Comprehensive Land Policy/White Paper (Land TWG). Mine Action TWG reported that consultation and dialogue with partners have been strengthened with more focus on strategic policy issues including the formulation of the next phase of the Clearing for Results Project. The Partnership and Harmonization TWG served as a mechanism to discuss the work of harmonizing planning, public investment expenditure and external financing, promotion of PBA and the use of country systems.
b) Programming and program design issues Programming and program design issues were among the subjects covered by TWGs. Agriculture and Water TWG reported that the development of harmonized SAW programs design was completed and approved by the two relevant ministries. Development of frameworks and mechanisms for implementing the harmonized SAW are also being considered although delayed by mobilizing of funds and securing of technical assistance. One of the constant themes for the Education TWG has been the monitoring of the implementation of program budgeting and the formulation of the Annual Operational Plan 2011. Likewise for the Health TWG, health financing specifically related to the Health Equity Fund has been regularly discussed and monitored by the TWG as a component of the national health financing plan and other financing mechanisms. The formulation of the National Program for Sub-National Democratic Development 2010-2019 has been completed and the 3-year Implementation Programme was formulated based on the National Program. Issues related to funding, funding modalities and governance arrangements will be taken up as reported by the D&D TWG.
c) Operational issues in strategy and program implementation TWG meetings also addressed operational issues related to implementation of sector strategies and programs. Discussions ranged from issues involving different thematic or reform areas to issues involving different levels of operations. The former includes sub-group discussion by the Education TWG on public financial management reform, decentralization and de-concentration reform and teacher training; the forum provided by the Partnership and Harmonization TWG for the discussion among stakeholders on on-going government reform programs such as the work on harmonization of planning, public investment expenditure and ODA, the work on promoting the application of PBA at sector which builds on the core reform programs; such issues addressed by the Private Sector Development TWG as on reducing the import-export lead time and the delivery of the SPS-related services to the private sector. The latter includes activities such as the sensitization and awareness promotion by the Mine Action TWG on mine action across other TWGs; briefing on progress of work from provincial level working groups under the Health TWG structures and the on-going engagement by civil society organizations with the Health TWG, and the mapping of support for sub-sectors by the Infrastructure and Regional Integration TWG.
d) Capacity development Activities were undertaken to address capacity development for ministries/agencies and TWGs including the secretariats. For instance, initiatives are on-going on strengthening the capacity of the secretariat of the Food Security and Nutrition TWG including training on aid effectiveness policy (aid management, reporting and communication skills, coordination); on-going training for secretariat by the Mine Action TWG. Functional review, training and professional training programs for ministries and agencies are initiatives that are going on under the leadership of the Public Financial Management TWG.
e) Aid effectiveness Reports from TWGs show that aid effectiveness was one of the constant themes discussed by most TWGs. The Education TWG planned to conduct a review on the status of the existing different aid modalities, technical cooperation and the existing PIUs in the sectors so that progress in addressing these can be monitored. Partnership Principles were developed and agreed/signed by government and development partners (Land TWG, Mine Action TWG) or in the process of being endorsed (D&D TWG). Led by the Partnership and Harmonization TWG, a concept note on promoting a programmatic approach in Cambodia was discussed and endorsed by government and development partners and resulted in a decision by the government on PBA as the government's preferred modality of implementing aid-financed cooperation activities. As of now a number of TWGs have expressed interest in pursuing PBA in the sectors or thematic areas (D&D TWG, Gender TWG; PPR TWG); the first PBA clinic was provided by CRDB/CDC to the Ministry of Women's Affairs in the second half of March, followed by a more comprehensive PBA clinic for all TWGs conducted in early April 2011. Others include actions that aim at increasing alignment and harmonization (Fisheries TWG, Forestry and Environment TWG), introducing a results-based approach in implementing sector strategies, and ensuring increased accountability between partners (nearly all TWGs).
2) Challenges All Technical Working Groups reported to have faced challenges during 2010. A number of planned as a consequence was not implemented on time or was postponed altogether. Common challenges include:
(1) Participation from other agencies/ministries There were activities which are cross-sectoral and involved participation from other agencies and ministries. Thus active participation from relevant ministries and agencies in TWGs and with sufficient level of decision-making power is important for the successful implementation of TWG work plans. The Fisheries TWG reported that the lack of an inter-ministerial support and participation could hamper the effort of the Fisheries Administration to reflect the importance of fisheries in the plans and strategies that affect the livelihood of the rural and poor people. Ensuring sufficient high level participation from relevant government institutions was necessary for the Forestry and Environment TWG to play a coordination and information role for the forestry sector. The process of finalizing the drafting of fundamental laws for the judiciary has been slowed and it is necessary that, as recommended by the Legal and Judicial Reform TWG, relevant agencies expedite the process.
(2) Resource Resource is another major challenge facing TWGs. The model court concept, planned to be implemented by the Legal and Judicial Reform TWG, was not sufficiently funded in 2010. For one activity in the 2010 work plan of the HIV/AIDS TWG, there was no technical and financial commitment from the members. The Infrastructure and Regional Integration TWG and the Agriculture and Water TWG similarly reported the issue of financial support in their work plan implementation. Although the National Forestry Program Action Plan was approved, implementation required financial allocation from the national budget (Forestry and Environment TWG).
Related to the resource issues, is the availability of or delay in procuring technical assistance. The Education TWG planned to develop a medium-term capacity development plan for the education sector, yet had to postpone because technical assistance appropriate for the task was not available. For the Agriculture and Water TWG, the SAW harmonized programs were approved; yet the development of a common framework and mechanism to implement the SAW harmonized programs was not implemented as planned because of the delay in mobilizing funds and procuring technical assistance for the task. The PFM TWG reported that the problem of availability of technical assistance and its slow procurement process led to the delay in designing a new system of de-concentrated budget.
(3) Competing priorities Competing priorities also were an issue that affected implementation by TWGs of planned activities. For example, Gender TWG reported delay in the activity of costing the Neary Rattanak 3 due to competing priorities that the Ministry of Women's Affairs need to implement. The development of a RWSSH sector guideline and the comprehensive mapping of support for the sector were the two activities planned for 2010 by the RWSSH TWG; yet they were overshadowed by a more important priority of formulating a National RWSSH Strategy. The strategy was finalized and subsequently endorsed and now the associated five-year operational plan is under preparation as well. For the Education TWG, competing priorities also postponed the conduct of aid effectiveness review for the sector, including a review of the status of current aid modalities, technical assistance and PIUs.
(4) Complexity of issues Complexities of issues involved also turned out to be a challenge that affects the implementation of planned activities by TWGs. A number of activities planned by the HIV/AIDS TWG have been delayed because of this reason, while the Legal and Judicial Reform reported facing similar problem in the implementation of its model court concept activity. The formulation of the 3-year Implementation Programme (IP3) had taken longer than expected, as it had to address a number of complex issues such as local development and financing. For other TWGs the lack of timely and updated information was indicated as challenge as well (IRI TWG, HIV/AIDS TWG, Education TWG).
3) Issues for consideration In the last consolidated report prepared by CRDB/CDC for the 17th meeting of the GDCC, October 19, 2010, two main issues were raised by TWGs for consideration. One was the availability of resources for implementing the work plans. Limited funding or uncertain financial commitment from partners had affected the implementation of planned activities. The second issue mainly concerned the operational/functional aspects of Technical Working Groups. Where a sector is well defined, implementation of TWG activities seems to go smoothly. But there have been issues which do not necessarily fall within clearly defined responsibilities of a Technical Working Group; and there are activities for which TWGs have to take on an increasing advocacy and/or facilitating role. This has only been complicated by the increase in the number of actors involved. To be meaningful, TWGs requires broad participation from stakeholders from both the government and non-government sector yet must ensure efficient functioning. These, among other practical issues, require guidance. The two issues continue to be relevant and are considered here.
Financial Resource The issue of funding TWG work plan implementation will continually be tackled by the TWGs. Experience over the years show that activities in the work plan of TWGs that were also drawn from the core activities of the ministries or agencies that lead the TWGs tended to be sufficiently resourced. Another set of activities in the TWG work plans were those related mainly to coordination, facilitation and partnership-building functions of the TWGs. It is this second set of activities that tended to be insufficiently funded. The block grant support, initiated by CDC/CRDB during 2008-2010, enabled TWGs to fill these funding gaps to an extent. Yet in the absence of such a support, as clearly indicated in the last report for the GDCC, implementation would suffer. While the government is making effort to increase support to TWGs to ensure that they function effectively, development partners that (co) facilitate TWGs are increasingly viewed as having important role to play in ensuring that the TWGs function properly. So far, the TWG mechanism has been evaluated as an effective mechanism for dialogue between partners; partnership requires between partners trust, transparency and the sharing of benefits (and risks as well).
Guideline on the functioning of TWGs The Guideline on the Role and Functioning of TWGs, issued by the government in 2007, was revised in response to the growing needs of TWGs for guideline newly emerging issues. The revised Guideline, which passed through extensive consultation with TWGs, development partners and Civil Society Organizations participating in TWGs, was finally endorsed by the government in November 2010. The Guideline aims, as it states, not to be overly prescriptive recognizing the specific contexts in which different TWGs are constituted and function. In the Guideline, suggestions are provided on practical issues pertaining to the functioning of TWGs such as linkages between the work of TWGs and the policy priorities of the government contained in such documents as the NSDP; the size and composition of TWG memberships; the standard agenda and format for a TWG meeting; conduct of the meeting; dealing with cross-cutting issues by TWGs; participation of Civil Society Organizations, etc.
4) Looking ahead to 2011
The reports submitted by TWGs to the GDCC secretariat indicate that all TWGs have prepared the 2011 work plan. The following table summarizes the main activities TWGs planned to implement in 2011.
III. Implementation of the Joint Monitoring Indicators
A set of Joint Monitoring Indicators (JMIs) was endorsed at the third meeting of the Cambodia Development Cooperation Forum (CDCF) in June 2010. It consists of activities that are implemented by TWGs, RGC ministries and agencies and development partners to achieve the agreed targets, the monitoring of which will be regularly conducted with clearly specified indicators. Managing for results had primarily been the basis on which the formulation of the JMIs rested. The set of JMIs that was subsequently endorsed at the 3rd CDCF clearly reflects this managing-for-results approach. The endorsed JMIs also include aid effectiveness actions associated with each TWG. While effort is being made to ensure that, where available, (output) indicators are included in the monitoring of the implementation of each JMI, the current monitoring focuses primarily on implementation at the activity level. This is to ensure that actions are being taken so that agreed outputs can be achieved and because information at the indicators' level only become available at a later stage once activities have been implemented (especially towards the next CDCF when progress on JMI implementation will be reported). Progress in JMI implementation Reports from TWGs point to steady progress in the implementation of JMI activities. With varying pace of implementation and results, all activities are being implemented. Despite challenges, compared to the previous reporting by TWGs for the 17th meeting of the GDCC (19 October 2010), the progress so far suggests that most TWGs are on track to achieve the targets (output in the JMI matrix) that were agreed at the third meeting of the CDCF. Status of the implementation of each JMI is detailed as follows. JMI 1: Planning and Poverty Reduction Activities under this JMI are being implemented towards (i) improved MOP and line ministries and agencies capacity to monitor the implementation of NSDP Update 2009-2013, including the preparation of the MTR in 2011 following the participatory approach used in NSDP preparation and (ii) strengthened institutional arrangements for harmonization of planning, public investment expenditures and development cooperation financing processes. Ministry of Planning Strategic Plan (MPSP). The MPSP 2009-2013 has been adopted. The AOPs for the last six months of 2010 and 2011 were prepared and agreed between MOP and DPs. The AOP for 2011 is now being implemented with support of the TWG-PPR and DPs.
Partnership Principles. Support for the preparation of a capacity development plan and its implementation has not yet materialized. Also, there have been delays in securing agreement on partnership principles.
M&E for NSDP Update. Work is in progress focusing at present on updating the NSDP Update and CMDGs indicators for priority ministries. A High Level Meeting at the SNEC has discussed the draft indicators on 17th March 2011. A workshop to crosscheck and validate NSDP M&E indicators that include CMDGs has been scheduled at the end of March 2011. Consultations with line ministries are on-going.
Harmonization work. Satisfactory progress by the Task Force for Managing the Process of Harmonizing Planning, Public Investment Expenditure and Cooperation Financing including an agreed new format and content of the 3 year rolling PIP 2011-2013; consultation with government agencies and DPs as inputs into preparing a situation analysis; the drafting of the situation analysis; consultation on the draft report of the situation analysis; and preparation of an action plan to implement recommendations from the situation analysis report.
JMI 2: Aid Effectiveness Activities are being implemented to ensure that "Harmonized and aligned development cooperation makes a demonstrable contribution to the delivery of RS-II, NSDP by furthering sector outcome-level results".
Facilitation of TWG Network. Facilitation support has been provided to the secretariats of TWGs. Retreats of the TWG network were conducted in September 2010 and April 2011 to share information, exchange of progress in relevant areas and to discuss and review policy documents (the revised TWG guideline, PBA concept note, decision 57 on implementing PBA).
PBA support. A concept note on programmatic approaches in Cambodia, following consultations, was endorsed at a GDCC meeting in October 2010. A series of meetings have been held to further refine the formats and substance of the support provided by CDC/CRDB (as a clinic) to TWGs, ministries and agencies that are willing to move forward in implementing PBA. A PBA clinic has been designed and agreed with the Ministry of Women's Affairs and started in March 2011.
"Making Partnership Effective" initiative. The "Making Partnership Effective" initiative (sequenced in a four phase format) has been completed in 2010. Findings have been shared with TWGs and development partners specifically during the last meeting of the TWG on Partnership and Harmonization in February 2011.
P&H TWG as forum. The Partnership and Harmonization TWG has been functioning as a peer review mechanism on a number of important policy initiatives including on the implementation of the government decision 57 on promoting PBA at sectors, promoting the use of country systems, the work on integration of planning, budgeting and ODA, and promotion of South-South Cooperation.
JMI 3: Education Activities are being implemented to ensure that "enrolment rate in lower secondary education increased". The agreed target of the JMI is expected to be reached by the end of the JMI implementation period. As of now, student promotion rate in primary education increased to 84.2% in SY2009-10. The promotion rate is expected to be increased as the target (85%) in 2010-11. The figure will be available in March 2012. Gross enrolment rate in lower secondary education stands at to 58.4% in SY 2010-11 while net enrolment increased to 35%. Grade promotion regulation implementation. The revised grade promotion regulation has been issued and its implementation enforced at all primary schools. Primary students were given a chance to be tested at the end of school year and at the beginning of next school year. Deployment of newly trained teachers. 95% of newly trained teachers have been deployed to under-staffed schools and in remote areas. Reduction of incomplete schools. Incomplete primary schools were reduced to 17.02% by December 2010. The number is likely to decline further during the JMI implementation period through the EFA Fast Track Initiative school construction program; the target is expected to be met. As of 2010, 262 (out of 582) school buildings have been constructed in incomplete and overcrowded primary schools; they now have become complete schools. Education indicators. With available information on population from NIS/MoP, the information has been used in EMIS to formulate key education indicators.
JMI 4: Health Agreed activities aim to "decrease maternal and new-born mortality rate."The target, agreed in 2010, of deliveries attended by skilled health personnel in the public sector for 2010 was achieved; for 2011 it is being set at 75% by the end of the year. The MOH plans to recruit at least 100 secondary midwives in 2011; in 2010, 95 secondary midwives and 244 primary midwives were recruited. The MOH and partners also committed to increase both government and total health partner funds to RMNCH in 2010-2011 and to ensure that these resources are reflected in the Annual Operational Plans at all levels. The AOP budget is shown in table below:
JMI 5: HIV/AIDS Activities are being implemented toward achieving (i) improved national response coordination & management mechanisms leading to efficient harmonization and alignment of stakeholder resources and efforts to address the priorities of NSP II & to inform the development of NSP III and (ii) stabilized and reduced risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
New TOR and updated membership of national and sub-national response mechanism. The development of the new TOR to reform the national and sub-national mechanism is planed in the fourth quarter of 2010 when the NSP III is launched. The 11 TWG now at the national level will be reformed to 7 TWG aligning with the 7 strategy written in the NSP III. The review of the FTA by the policy board is scheduled in the last quarter of 2010.
Results-based plans with indicators. These will be developed after the NSP III is launched in October 2010.
Guideline for national and sub-national response mechanism. The guideline will be developed after the NSP III is launched. Orientation of key stakeholders. The orientation and the RBM and leadership training is delayed due to the delay of the proposal approval from the CDC/CRDB.
2010 NASA. The 2010 NASA will be started in the last quarter of 2010. The NAA will take the lead on developing the technical support to the 2010 NASA.
Dissemination of NASA results. The NASA result will be available in April 2011.
Round 10 proposal of GFATM. The GFATM R10 proposal was developed with the participation from the key stakeholders and aligns with the NSP III 2011-2015.
JMI 6: Food Security and Nutrition Target is to ensure that "through improved evidence, emergency response, and coordination food security and nutrition of the poor and vulnerable are improved".
Food Security and Nutrition Information Management Taskforce A promotion workshop was organized early this year to inform relevant stakeholders about the existence of the Task Force and to ask for cooperation for synergy. Apart from this, a series of meetings have been convened to discuss the formation of a food security data analysis team and the establishment of an integrated food security monitoring system. A list of indicators for monitoring have been drafted and discussed. At the same time, relevant line agencies have already nominated their representatives to join Task Force upon CARD’s request.
Capacity of the food security and nutrition analysis team Food Security and Nutrition Data Analysis Team (FSN-DAT) was established with a TOR which was discussed and endorsed in the meeting. To equip the team with analytical skills, a first training on food security M&E for the analysis team was conducted. In addition, the team also receives on-the-job trainings. One of the main achievements of the team is the production of the quarterly FSN bulletin and FSN annual report both of which have already been endorsed and disseminated. At the moment, the 2nd FSN bulletin is underway using the newly available data/statistics including CSES 2009, and administrative data.
JMI 7: Agriculture and Water Most of the agreed activities are being implemented to achieve the goal of "enhanced agricultural productivity and diversification and improved water resource development and management". Public expenditure review. Public expenditure review for agriculture and water sector was completed.
Roadmap for SAW implementation. The draft TOR for the development of a SAW implementation roadmap was finalized following consultations. Funds for technical assistance have been mobilized and procurement is underway.
Pooled basket fund. Implementation of this activity will begin following endorsement of the recommendations from the SAW Implementation Roadmap.
Increased number of functional Farmer Organizations. Up to now 200 Agricultural Cooperatives have been established and registered as legal entity in 23 provinces.
Increased irrigated land area. Irrigated area increased by 53656 ha in 2009.
Increased number of functional FWUCs. By 2010, MOWRAM has formed and operated 370 FWUCs with irrigated area of 175 769 ha (rainy season) and 72368 ha (dry season) in 2009.
JMI 8: Land The goals comprise (i) improved land administration and land tenure security and (ii) Increased equity in land distribution. Policy for land administration, distribution and management
Land registration strengthened
Social land concession
JMI 9: Forestry Activities aim to ensure that "forest cover of country land area will be maintained by increasing of quality and quantity through better management of forest resources".
Reforestation of degraded lands. So far, 26,775 ha were planted. The annual work plans for 2011 for 5 Cantonments have been developed and supported. Central FA work plan 2011 has also been supported.
Forest estate demarcation. 750 Km of forest estate has been demarcated and four Protected Areas have been demarcated (Preah Suramrith-Kosumeak, Kirirom, Kep, Sam Lot).
Community forestry and protect areas. 106 community forestries have been approved by MAFF as the approval process has been significantly improved and 14 Community Protected Areas by the MoE. There are 288 sites with 587,576 ha under survey for potential establishment of community forestry. This activity will continue well into 2011.
REDD Readiness Roadmap. The REDD Road Map has been approved by UN-REDD and a grant of $3M has been secured.
JMI 10: Fisheries Activities are being implemented so that "fisheries plans in support of food security, livelihoods and economic development improved".
Strategic Planning Framework The 10-year SPF has been endorsed by the TWGF on 05 July 2010 and approved by MAFF in mid March 2011. The Khmer language version of the document has been finalized and will be published soon. SPF Implementation The Annual Fisheries Action Plan 2010 and 2011 have been developed and implemented based on SPF targets despite not all activities being funded. Approximately 80% and 70% are funded by DPs for the Annual Plan 2010 and 2011, respectively. The funding support to fisheries is based on the SPF and is a significant step toward PBA.
Sub-National fisheries planning processes in line with SPF The Sub-National fisheries planning processes (called the ToRs for Implementation of Fisheries Cantonment Planning and Coordination) has been endorsed by the TWGF and forms part of the SPF. The ToR has been fully aligned within D & D policies and plans. At present this sub-National planning process is being piloting in 6 provinces. This will require substantial time, financial resources and effort to enable the sub-National staff and the Fisheries Administration to deliver an effective service at the sub-national level. In particular, staff capacity at sub-national level is being developed through targeted training programme.
JMI 11: Mine Action Implementation of agreed activities aim at achieving "reduction in the number of mine/ERW casualties and increased land released to support to rural development".
Improved national capacities in coordinating, planning and monitoring mine clearance plans The CMAA has initiated the alignment of mine action planning with sub-national development plan and commune investment program (CIP). Once finalized and applied, this alignment will ensure that mine action planning and clearance priorities directly respond to community development objectives. DPs will be briefed on this new operational guideline at the 4th April workshop. The Partnership Principles support DPs’ alignment to the national mine action strategy. Consultation on the draft partnership principles reached its advanced stage. Comments from most development partners have been addressed. We are gearing towards the right path with the signing of the Partnership Principle s and a final document will be signed in 4-5 April 2011. Six DPs have indicated their intention to sign on April 4th.
Use of land release methodologies The CMAA has been promoting the use of BLS and Land Release methodologies with operators, MAPU (workshops) and donors (TWG + bilateral) resulting in operators using BLS data for their planning purposes and donors looking forward the availability of data which is a positive sign of donors using government data for their planning purposes.
Baseline Survey Phase I and II Phase 1 (21 districts) of the Baseline Survey is being completed and Phase 2 (42 districts) will completed in 2012. The Baseline Survey will provide baseline information on the remaining threat that will enable better targeting of clearance and maximize the use of assets through Land Release methodologies. Funding for the BLS phase 2 and 3 in 2011 and 2012 have not yet been secured and might jeopardize the completion of the BLS in time. Mine Risk education program Specific Mine Risk Education (MRE) messages and activities tailored to the needs of the remaining male and female high-risk groups have been developed and printed for use by MRE operators through 3 MRE coordination meetings. Nine notational MRE coordination meetings and a join monitoring field visit under the leadership of the CMAA have enabled redefining MRE approaches and implementation mechanisms with greater involvement of national, sub-national and local entities. Mine/ERW affected communities have increasingly been empowered in MRE, support to mine action, victim assistance, community development and socio-economic reintegration through micro-loan and other employment opportunities. Thousands of requests for the mine/ERW collections and destructions have been timely responded by demining operators through Mine/ERW networks capacity development. JMI 12: Private Sector Development Activities under this JMI have as goals (i) reduced lead time for import and export and (ii) More efficient delivery of SPS-related services to private sector traders. Reduced lead time for import and export:
More efficient SPS-related services:
JMI 13: Infrastructure and Regional Integration Activities are being implemented to ensure that "road maintenance is adequately implemented". A draft "Overview on Transport Infrastructure Sectors in the Kingdom of Cambodia version 2010" under financial and technical support from JICA was developed. Circulation among partners for comments wad completed and now is being printed.
JMI 14: Rural Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygine The goal is "improved access to water supply, sanitation and hygiene in rural areas". The National Strategy on Rural Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygiene has been finalized.
JMI 15: Public Administration Reform Activities within this JMI aim to lay "foundations to deepen and widen the Administrative Reform in place".
Approval of NPAR. NPAR is available for broad dissemination in both Khmer and English. M&E framework is being drafted for consultation.
Multi-year development agreements. An implementation agreement covering 2011 was signed with GIZ in December 2010. A similar agreement covering 2011 was signed with Danida in March 2011. Implementation of two-year agreement with ADB is pending subject to fulfillment of effective conditions. WB support focuses on short term technical assistance. Multi-year arrangement is unlikely.
HRM process. HRM policy has been finalized and will be referred to national seminar in late April for endorsement. Documents on all eight components of HRM policy are being drafted for consultation at the seminar. Results will be used for preparing HRM Manual specifying HRM components. Consensus has been reached on strengthening four HR processes (recruitment, promotion, retirement and examination).
HRD policy framework. HRD policy has been drafted and is ready for consultation with stakeholders. HRD Manual specifying components and related processes is being drafted. Labor market study and fiscal space. The study on fiscal space has been completed, while the study on labor market is almost also completed. Outstanding item is the benchmarking of selected back office positions to implement the work on guide on operational reviews.
Guide on operational reviews. There has been some delay in completing the guide due to complexity of the issue. Draft guide should be completed by the end of March.
Operational review pilots. This activity is awaiting the finalization of the guide. It also faces the challenge of mobilizing necessary resources to train ministries in the use of the guide. The pilot is likely to take place in two ministries (MEF and MPT).
Options for sequencing compensation reform. Study tours are undertaken to inform on best practices in the region. The options will be developed in June.
JMI 16: Legal and Judicial Reform The target of this JMI is "improved court functioning". Yet successful implementation of the JMI activities and reaching the target is being challenged. Constraints have ranged from the untimely provision of technical support to difference over substantive issues that will be covered in the laws. It has been suggested by the TWG that a working group should be established to identify ways to over these constraints.
Fundamental laws of the judiciary. A review of three draft laws is being conducted. The fundamental laws cannot be completed with just technical assistance. Institutional stakeholders have differing positions on the substantive issues in the laws that require policy guidance.
Model court. Progress has been made on this activity. The development of court registers has been completed and training of court registers is being developed. There still yet different perceptions among stakeholders on what the Model Court program entails. The CLJR should meet, it is suggested, as matter of urgency to give directions on court reform.
JMI 17: Anti-Corruption The aim is to "combat corruption". The following measures/activities have been implemented.
Anti Corruption Institution. The ACI has been established comprising a National Council Against Corruption (nomination of the president, vice-president and 9 seating members) and the Anti-Corruption Unit (the nomination of its president, and vice presidents). A Sub Decree on the Organization and Functioning of the Anti-Corruption Unit, a Sub Decree on Logo and Seal of the ACI and a Sub Decree on Annual Budget were also issued.
Education and public awareness on corruption. The National Seminar on dissemination of Anti-Corruption Law and Assets and Liabilities Declaration Forms were public organized starting from December 2010 with all state institutions and ministries the National Assembly and the Senate and with provinces and the capital city as well.
Prevention of corruption. Measures have been developed by the Anti Corruption Unit including, among others, a five year Action Plan 2011-2015 for the National Council Against Corruption, a two year Anti Corruption Action Plan 2011-2012 for the Anti Corruption Unit, Assets and Liabilities Declaration Forms, and press conference results of every anti corruption operation.
Zero tolerance principle on corruption. Investigations have conducted and suspects of corruption cases and their networks have been arrested and sent to court. Other remaining cases are being investigated and monitored for prosecution.
JMI 18: Decentralization and De-concentration The goal is to ensure that "public service delivery has been brought closer to the citizens through institutionalization of the Sub-National governance structures and systems".
Three-Year Implementation Programme The IP3 was completed and adopted by the NCDD in its 5th meeting on November 30, 2010. Development partners have reviewed the IP3 and funding appraisal was conducted. In the process, a number of issues were raised and a roadmap on addressing these issues is being developed by NCDD. Due to delays in finalizing and appraising the IP3, implementation could not start in the first quarter of 2011; implementation of the IP3 is expected to commence in April.
Integration of structures and systems at sub-national levels The process of integrating/shifting existing Salakhet (23 provincial cabinets) and the Sala Reach Theany (Phnom Pech) personnel was completed by end of August 2010. They have become official in the Provincial Management Administration since then. However, Excom is still in place -- until the Provincial Management Administration is able to take over all activities. NCDD will evaluate and determine the time for the final closure of Excom.
Integration of personnel with capacity development The integration /shifting of staff and functions process in the province and district was completed in August 2010. Planned capacity development has been postponed due to the financial shortfall at the beginning of IP3. However, the trainings on sub-national planning process have been conducted for both provincial and district levels. The provincial and district planning formulations are under process. Key legal documents to support sub-national administrative reforms Prakas on the division of roles and responsibilities of the Board of Governors and guideline on the division of roles and responsibilities of the Technical Facilitation Committees have been formulated and have been put into effect. Inter- Ministerial Prakas of MoI and MoP on Development Plans and 3 year Rolling- Investment Programme and the Technical guidelines for Development Plans and 3 year rolling investment programmes for SNAs have been approved by NCDD and put into effect.
Law on Sub-National Finance Regime and Property Management The draft Law on Sub-National Financial Regime and Property Management has been adopted by the NCDD in its 5th Meeting and further forwarded to the Council of Ministers for review and approval. The Council of Minister approved the draft law on January 21, 2011 and will be sent to the National Assembly and the Senate for approval by April 2011.
JMI 19: Public Financial Management Building on the foundation that has been laid, activities under this JMI aim at "sustaining and strengthening budget credibility and improving financial accountability". The implementation of the Public Financial Management Reform Program is progressing. Significant progress has been made in improving financial accountability in key areas. Budget credibility has been maintained.
A draft revenue paper is being finalized and the draft taxation law on oil and gas is being developed. Revenue forecasting and collection have been further strengthened. A change management strategy and communication plan and a change management sponsor roadmap are being developed. There have been further improvements in the recording of payments and orders. Bank accounts have been rationalized and the use of commercial banking system has been increased.
Yet there has been delay in the design of a new system of de-concentrated budget with financial management roles as the technical assistance necessary for implementation has not been provided on time due to unavailability of international consultants and the associated slow process of procurement. To move forward, the procurement process should be expedited and consideration should be given to procuring TA firms rather than just individual TA and the TOR for the technical assistance support should be prepared. The implementation of the FMIS and its related activities (such as awarding of FMIS contracts, design of business process; FMIS system software) in pilot ministries has not yet started as the preparation has taken longer than expected and due to the long process of evaluation and approval. The conduct of a Functional Review of MEF and line ministry finance and accounting operations (FMIS pilot ministries) is behind schedule as no TA has been provided on time. On the other hand, the Functional Review is being addressed with cautious approaches to ensure smooth change and sustainable capacity. The provision and development of training programs for MEF and line ministries (including professional training programs such as on procurement, accounting, auditing and ICT) are being implemented slowly. The arrangements for the conduct of the trainings are time consuming and there remain a number of issues that need to be addressed such as flexibility on financial support for trainers who are civil servants.
JMI 20: Gender Activities are being implemented toward reaching "sustaining and strengthening budget credibility and improving financial accountability".
Quality social and legal services for women
Law enforcement to prevent GBV and protection of victims
Coherent system to monitor legal protection mechanisms for DV/GBV
Challenges in implementing JMI activities
The following table provides a snapshot view of the areas and nature of challenges faced by TWGs in implementing the agreed JMI activities. Chief among those are resource-related challenges which have led to the implementation of agreed activities being delayed or have forced TWGs to divert or choose between endorsed priorities. Several TWGs indicated financial challenges that directly concern the proper functioning of the TWG secretariats. As a working arm of TWGs, the ability of secretariat to support TWGs in the performance of their roles (such as implementing and monitoring JMIs for example) needs immediate attention.
The second set of challenges stems from the complexities of issues that are being addressed. This has in some cases led to implementation being behind schedule because of the need for more study and information to better formulate responses. Notable is the difficult and complex issues of governance arrangements that emerged during the appraisal of the 3-year Implementation Program as reported by the D&D TWG. These issues have been taken upon and currently the NCDD is in the process of developing roadmaps to address them before implementation can start.
Challenges arising out complexities of issues at hands are related with capacity levels of the TWGs that are responsible for implementation of activities. The Fisheries TWG, for instance, reported the challenge of staff capacity especially at the sub-national levels, in ensuring that sub-national fisheries planning processes are in line with the Strategic Planning Framework endorsed by the Fisheries Administration. Growing complexities of issues that are being addressed have also been compounded by the fact that some JMI activities involve sub-national levels. For instance, Mine Action TWG indicated the complexity in aligning mine action planning with the sub-national development plans and commune investment plans. PFM TWG also reported the delay in the design of new system of de-concentrated budget and financial management roles and responsibilities (develop budget entity and internal control procedure framework, deepen classification reforms, and identify appropriate accounting standard). TWGs whose activities encompassed sub-national entities have also faced issue of financial constraints (Fisheries TWG in the area of sub-national fisheries planning, Mine Action TWG on the conduct of a Baseline Survey).
The final set of challenges came from the fact that JMI activities required coordinated actions from various ministries/agencies and TWGs. These are mainly issues of cross-cutting nature and related to the government's core reforms which require cooperation from relevant agencies. In other cases, building consensus among stakeholders on sensitive reform issues has often been a stumbling block before activities could be implemented (the PPR TWG, RWSSH TWG, F&E TWG, PAR TWG, PFM TWG).
Implementation of the aid effectiveness priorities The table below provides an overview of the implementation of the aid effectiveness priorities associated with each TWG.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||