|
Power Point Presentation
|

|
|
|
|
Outline |
 |
-
I. Macroeconomic Performance
-
II. Fiscal Developments
-
III. Development of a robust financial sector
-
IV.
External sector performance
-
V. Social development
and poverty reduction.
-
VI. The way forward
|
|
|
|
|
I. Macroeconomic
Performance
|
|
|
|
1. Macroeconomic Performance
- Positive and progressive
changes over the past decade:
- Sustained and steady
economic growth;
- Stronger integration with the region and the rest of the
world;
- Sharp and spatially widespread reduction in poverty levels;
- Steadily improvement in fiscal discipline and management;
- Measurable improvements in various social indicators:
expansion of primary education; reduction in MMR and IMR;
reduction in communicable diseases; improved access to safe
water and sanitation.
|
|
|
|
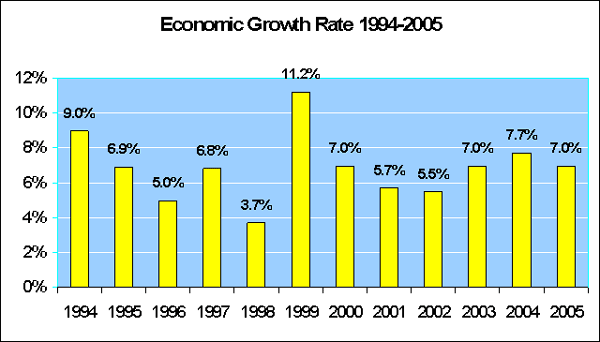
Cambodia's Performance
|
|
|
|
Sectoral Contribution to
GDP (1999-2004) |
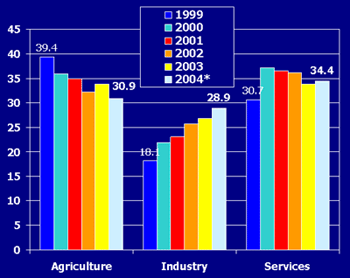
Source: Ministry of Planning
National Accounts of Cambodia 2004
* Preliminary estimates |
- The structure of sectoral shares in GDP have been
changing gradually throughout the 1999-2004 period,
reflecting the diversification of Cambodian economy
- The share of agriculture in total income is slowly
falling, but instead the manufacturing activities are
begun to rise.
- Although share of agriculture in GDP is still the
highest in average, but it has been steadily declining
from 39.4 percent in 1999 to 30.9 percent in 2004
- The share of industry in GDP has increased from 18.1
to 28.9 percent respectively.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Fiscal incentives for
garment sector
-
Particularly for
garment exports, the Royal Government has provided
financial incentives to support this sub-sector after
the end of Multi-Fibre Agreement in early 2005.
-
The RGC exempted
payment of profit tax for 2 more years, resulting in
loss to budget revenue of approximately CR71.5 Billion
in 2006 and CR106.2 Billion in 2007. This does not
include custom duties exemption of approximately
CR1,211.8 billion a year.
|
|
|
|
|
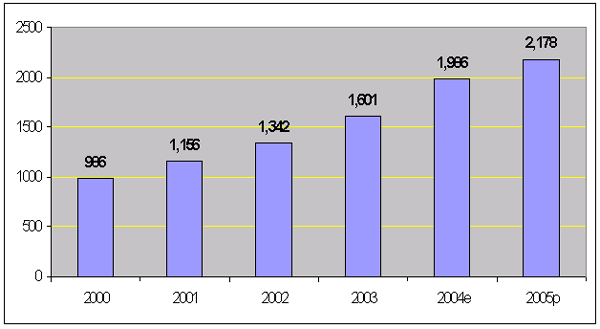
Cambodia's Garment Exports (million US$)
|
|
|
|
1. Macroeconomic
performance (cont…)
-
Medium term outlook is
good;
-
The prospect of the
robust economic growth will remain valid as Cambodia’s
off-shore oil and gas exploration provides strong
impetus to economic development of Cambodia.
-
The government approved a
number of infrastructure and real estate projects, which
would imply that construction activities will drive GDP
growth in the next 5-10 years;
|
|
|
|
|
1. Building foundation
for sustainable development
|
|
|
|
|
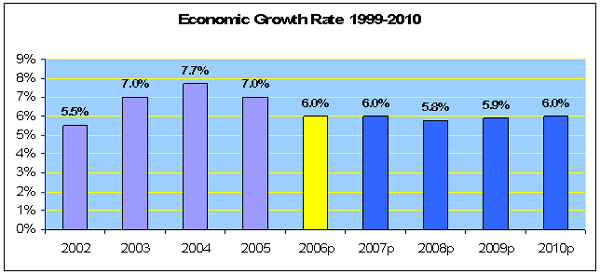
Overall Economic Growth
Outlook
for 1999-2010
|
|
|
|
|
II. Fiscal Developments |
|
|
|
2. Public Financial
Management Reform
|
|
|
|
|
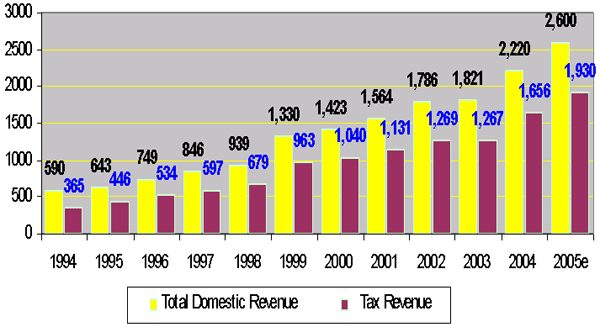
Revenue: 1994-2005
(in billion of Riels)
 |
|
|
|
2. Fiscal Developments
-
The fiscal performance
in 2005 has been good, with improved revenue
mobilization and expenditure rationalization.
-
On nominal term,
revenue increased by 22% in 2004 and 17% in 2005;
-
On real terms,
domestic revenue in 2005 reached 11.7 percent of GDP,
compared to 7.6 percent of GDP in 1995 and 11.3 percent
of GDP in 2004.
-
On real terms, tax
revenue increased from 5.3 percent of GDP in 1995 to 8.7
percent of GDP in 2005, an increase of 3.4% of GDP.
|
|
|
|
|
Total Central Government Current
Expenditure: 1994-2005
(in billion of Riels)
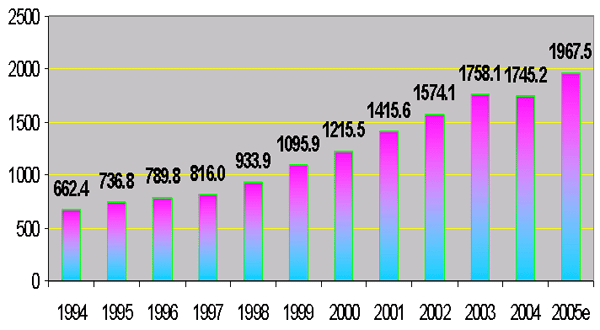 |
|
|
|
2. Spending on
Infrastructure
-
RG attaches great
importance to infrastructure development;
-
Studies indicate that
decreasing the distance from the village due to good
road by one kilometer will enhance productivity by about
30 thousand Riel per hectare;
-
Land with access to
irrigation facilities during the dry season has 15
percent greater rental value and 10 percent higher sale
value than land without irrigation;
-
From 2000-2005 the
disbursement for infrastructure and its maintenance
amounted to about 1,324 billion riels.
|
|
|
|
|
Infrastructure Spending
(in billion of Riels)
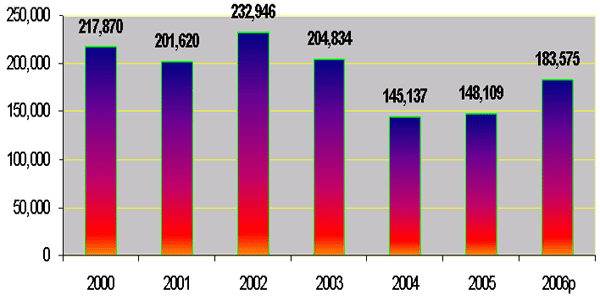
|
|
|
|
Road Maintenance Fund
(in billion of Riels)
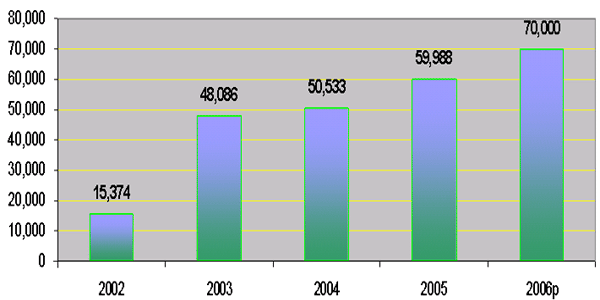 |
|
|
|
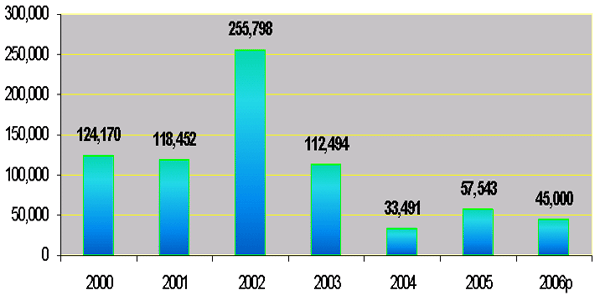
Road Expenditure
(in billion of Riels)
 |
|
|
|
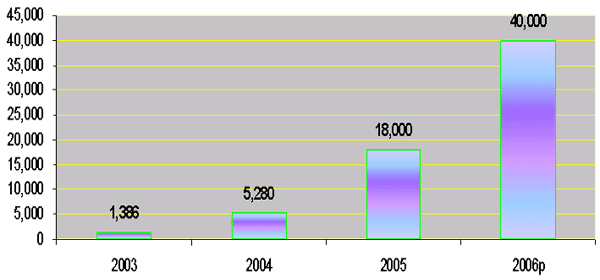
Irrigation Expenditure
(in billion of Riels)
 |
|
|
|
2. Spending on Infrastructure (cont…)
- For the period 2004-2005, the Royal Government
disbursed 270 billion riels for road-bridge
infrastructure and 23 billion riels for irrigations;
- In 2006, the Government has allocated 115 billion
riels for road-bridge infrastructure and 40 billion
riels for irrigations
|
|
|
|
|
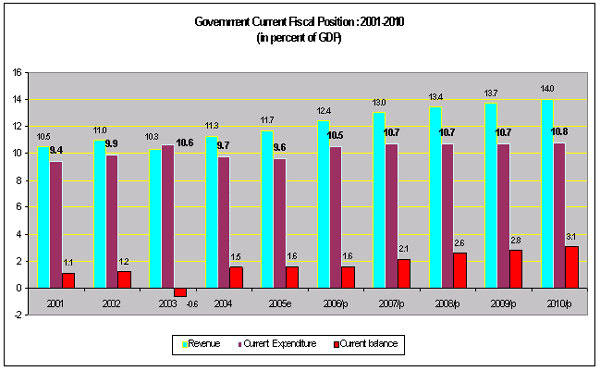
2. Medium Term Fiscal Plan
 |
|
|
|
III. Development of a
robust financial sector |
|
|
|
3. Monetary Policy and
Performance
-
Banking reform will
continue;
-
Greater confidence in
the banking system leads to broad money recording a
robust growth of 20 percent in 2005, due to the increase
in foreign currency deposits and credit to the private
sector.
-
Credit to private
sector rose by 40%, driven by the construction of hotels
and real estate.
|
|
|
|
|
3. Financial Sector Analysis
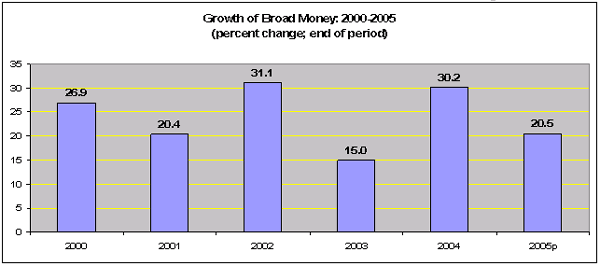
-
In 2005, M2 grew 20%, foreign
currency deposits of residents remained the most important
counterpart to monetary expansion, accounting for more than half
of the annual increase in broad money.
|
|
|
|
3. International Reserves
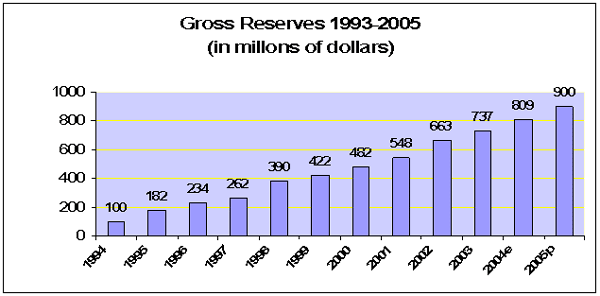
|
|
|
|
3. Foreign Investment
-
The proposed
investment projects include:
-
US$2 billion new town
project near Phnom Penh,
-
US$200 million oil
refinery,
-
US$180 million cement
factory,
-
US$34 million hotel
and golf club,
-
US$30 million office
building,
-
US$27 million power
station,
-
US$19 million dry
port,
-
US$13 million
industrial zone,
-
US$3 million tobacco
factory,
-
US$5 million cigarette
factor,
-
US$9 million sea port
at Kampot and others.
|
|
|
|
|
4. Inflation
-
Despite high oil
prices, the Royal Government has been successful in
maintaining inflation under check and ensuring stable
exchange rate in general.
-
Inflation reached 5.8
percent at the end of 2005. This is in the range that
can be managed.
|
|
|
|
|
4. Trends in inflation
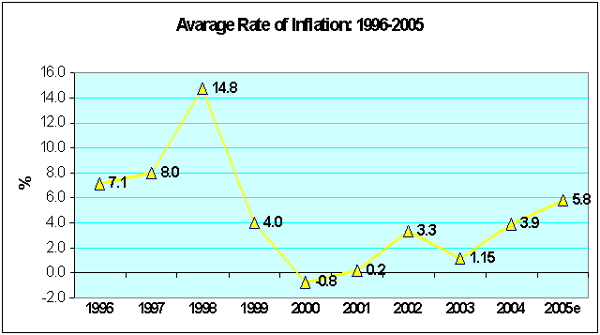
|
|
|
|
4. Development of
Microfinance,
insurance and capital markets
-
Microfinance has
transformed former Khmer strongholds into prosperous
farms;
-
The government will
introduced life insurance;
-
Draft laws and
regulations are being prepared for the development of
bond markets and stock exchange;
-
Accounting and
auditing standards were introduced and training is
underway to improve corporate governance.
|
|
|
|
|
IV. External sector performance |
|
|
|
4. External sector
performance
-
There were signs of
improvements, despite high oil prices;
-
Provisional 2005 data
indicated that the overall balance registered an
increased surplus of 1.1 percent of GDP, compared with a
surplus of 0.9 percent of GDP a year earlier;
-
This improvement
resulted mainly from a larger inflow into capital and
financial accounts as against last year's performance,
which was more than offset by the increase in the
current account deficit.
-
Domestic exports are
expected to increase by 9.8 percent, while import will
increase by 17.6 percent.
-
Exports of textile,
clothing and footwear, which accounted for 80 percent of
Cambodia's domestic exports, continue to expand.
-
Non-garment exports
were estimated to have increased at a faster pace than
the garment sector, albeit from a very low level, and
produced only about 13 percent of Cambodia's total
export earnings.
-
This group includes
traditional agricultural commodities such as rubber,
wood products, fishery products, and paddy rice.
|
|
|
|
|
Cambodia's Performance
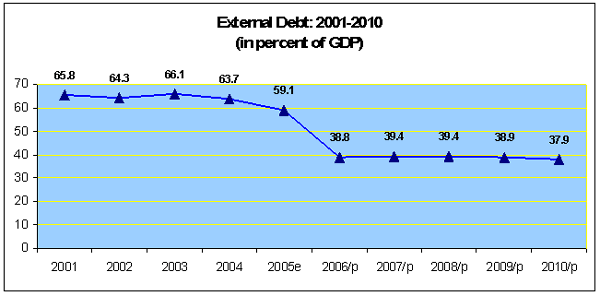
|
|
|
|
|
V. Social Development
and Poverty Reduction |
|
|
|
5. Social Development:
Education
-
Cambodia has made
impressive progress in financing and reforming the
education sector, with the support of the development
partners;
-
A focus on primary
education, backed with rising public spending, has
resulted in more schools and trained teachers, lower
direct costs to households;
-
From 1994 to 2005,
spending on education has increased more than four times
in nominal terms, from 61.6 billion to 350.8 billion CRs
respectively;
-
The government
spending has benefited to the poor;
|
|
|
|
|
Spending for the Ministry of
Education: 1994-2005
(in billions of Riels)
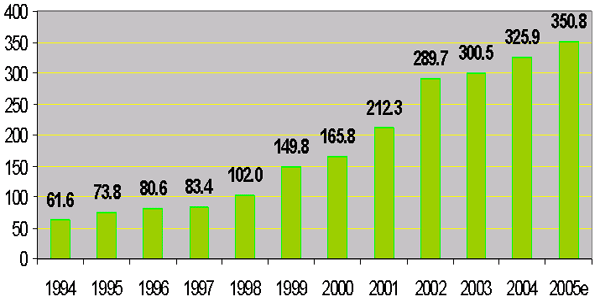 |
|
|
|
5. Social Development:
Education (cont…)
-
Increasing net primary
enrolment rates from 84% in 2000 to 91% in 2004
(particularly for girls and poor children).
-
The percentage of
children needing to repeat grades has fallen
considerably from 26 percent in 1997 to 10 percent in
2003.
-
Concerns for improving
quality at all levels however continue and have to be
addressed.
|
|
|
|
|
5. Social Development:
Health
-
Significant progress has been achieved in the Health sector as well.
-
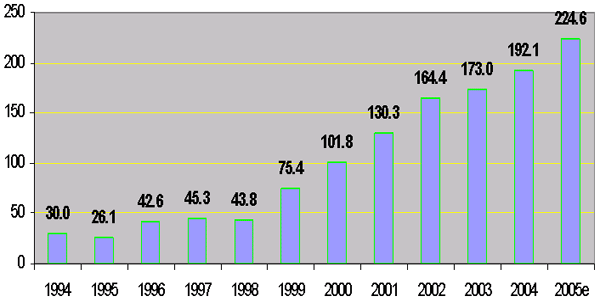
Health spending has also risen significantly from 30 billion CRs in 1994 to 224.5 billion CRs in 2005 (an increase more than six times).
-
All health indices have shown considerable improvement but they are still high;
-
IMR has declined from 93 per 1,000 live births in 1998 to 66 per 1,000 live births in 2003;
-
Under 5 Mortality Rate declined from 124 to 97 for the same period;
-
Life expectancy at birth increased for men from 52 to 60, and for women from 56 to 65 years.
|
|
|
|
|
Spending for the Ministry of
Health: 1994-2005
(in billions of Riels)
 |
|
|
|
5. Social Development:
Health (cont…)
- A spectacular success story is the
rapid decline in prevalence of HIV/AIDS (down to 1.9
percent among adults aged 15-49 in 2003, from 3 percent
in 1997), brought about RGC's highly focused commitment
and excellent collaboration with and among external
development partners.
- TB and Malaria prevalence is on the
decline.
|
|
|
|
|
5. Poverty Reduction
-
Poverty in Cambodia has fallen by 10-15 percent between 1994-2004. Poverty headcount reduced from around 47 percent in 1994 to 35 percent in 2004.
-
If based on geographic samples of surveys in 56% of total territories, the poverty headcount reduced from around 39 percent in 1994 to 29 percent in 2004.
-
Per capita household consumption has risen 32 percent in real terms.
-
Critical problems for the urban poor revolve around security of housing rights and opportunities for gainful income generation.
|
|
|
|
|
The Way Forward
-
PFM Reform is crucial
for Cambodia’s development;
-
Mainstreaming the
Priority Action Program (PAP);
-
Program budgeting
linking policies to financing;
-
Public accounting
reform;
-
State enterprise
reform – performance;
-
Performance based
management;
-
Mainstreaming
Meritocracy to improve government bureaucracy;
-
Ensuring sustained
growth;
-
Agricultural
development for poverty reduction.
|
|
|
|
 |
Thank you for attention! |
|
|
|








