|
Aid Effectiveness
in Cambodia
The Implementation Challenge
H.E.
Chhieng Yanara
Secretary General
CRDB/CDC
Cambodia Development Cooperation Forum (CDCF)
June 20 2007
|
|
It
is time to implement the commitments we have made
“There has been a significant effort
made to change the manner in which aid is delivered…yet the outcome
in terms of development results has not always been immediately
evident. In short, too much heat and not enough light.”
AER, p 2
“The focus of both Government and
development partners must be placed on the implementation of
existing frameworks.”
AER, p 45
|
|
The AER: Evidence-based aid management
- Establish the aid-results
transmission mechanism
-
A common vision of the policy agenda
& associated reforms
-
Comprehensive planning, budgeting, execution and monitoring
-
Transparent & accountable resource use via universal access to
on-line data
-
Use of
donor’s own data for evidence-based analysis
-
Use of data
and reports to monitor the H-A-R Action Plan
-
Use of data
to establish a set of H-A-R indicators
-
Priority
setting and policy recommendations based on empirical findings
that are directly linked to NSDP implementation and results
|
|
Trends in Aid Delivery
A decline from USD 610m in 2005 to
USD 595m in 2006 Significantly reduced loan disbursements
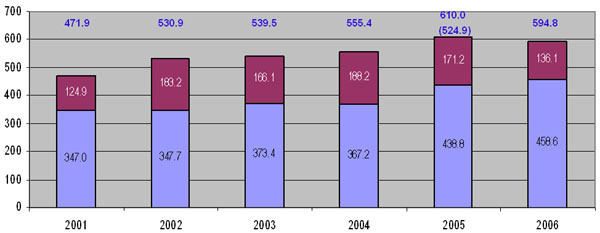
…but we need to work together to improve the data |
|
Alignment &
predictability – positive developments
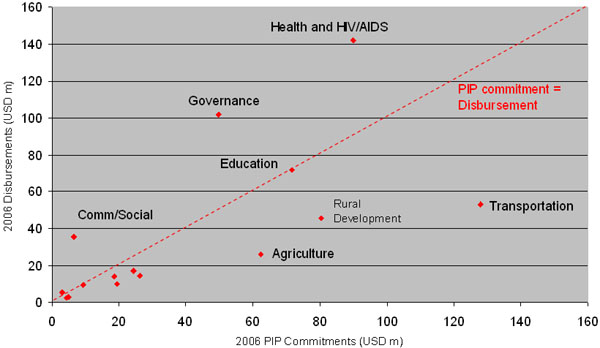
…but more progress is
required |
|
Technical
cooperation – what impact? |
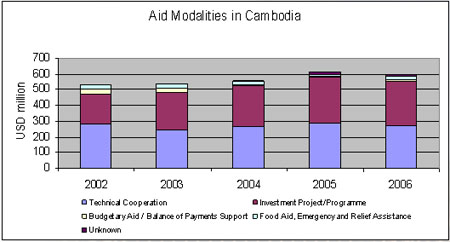 |
“It
may be time to re-think the use of technical cooperation...
…in the context of a
partnership-based approach…there can be sharply diminishing
marginal returns in the use of technical cooperation experts… |
| |
|
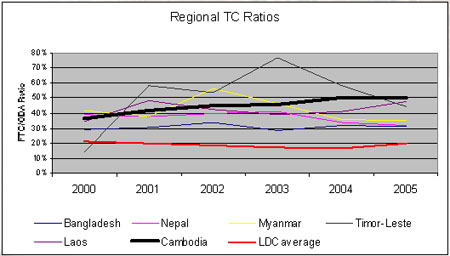 |
…in
the current aid environment, technical cooperation may be
associated with partnership-based efforts to support the
national programme…
…the rationale for TC provision
remains the same: capacity development.”
AER p43 |
|
|
Concentration & Fragmentation in Aid Delivery
-
By
global and historical standards, aid in Cambodia is
excessively fragmented
-
Empirical analysis confirms the extent of the problem
-
“Business as usual” is not an option
|
|
Sector |
# Projects
|
# Donors |
| Health |
109 |
22 |
| Education |
79 |
21 |
| Governance |
67 |
20 |
| Rural Dev't |
49 |
20 |
| Agriculture |
58 |
16 |
| HIV/ AIDS |
23 |
14 |
|
“Each partner is inclined to
participate in every decision and to join every policy
dialogue…[becoming] increasingly focused on the results of their own
projects, losing sight of the broader and more strategic objectives
of the national programme” AER p6
|
|
Addressing
Concentration, Reducing Fragmentation
-
Progress on
co-funding partnerships must be acknowledged
-
Renewed commitment to advancement of
SWAps and programme-based approaches
-
Implementation of the TWG Guideline
-
donor division of labour
-
joint reporting, monitoring, review
-
pooled funding through RGC systems
-
rationalise technical cooperation
|
|
Policy Recommendations
-
‘Action Plan overload’ -
no new initiatives
-
More focus on
implementation and results
-
The existing policy
framework is sufficient
-
Division of labour (TWG Guideline)
-
Consolidated resource envelope (PFM Reform)
-
Reduced fragmentation (TWG Guideline)
-
Focus on monitoring for results (TWG Guideline)
-
Capacity for aid management (Strategic Framework)
-
Institutional arrangements and mutual accountability (Strategic
Framework & TWG Guideline)
|
|
1.
Implement the TWG Guideline
- A common vision and a common
strategy
-
Consolidated RGC and aid funding framework
-
PBAs and a
‘donor division of labour’
-
Rationalised use of technical cooperation
-
“Default
approach” to aid delivery & management
|
|
2.
Implement the Strategic Framework for Development Cooperation
Management
Closer MEF – MoP – CDC collaboration
-
Promote
alignment through the PIP & AER analysis
-
Enhance
financial planning (CDC-MoP-MEF)
-
CDC as a
co-signatory for all new projects
-
CDC-donor
consultations to promote aid effectiveness
-
Use of CDC
Database for evidence-based analysis
|
|
3. Technical
cooperation in the new aid environment
Measures to increase the
effectiveness of TC are closely associated to recommendations on
TWGs and fragmentation
-
A demonstrated link to capacity development
-
A
role in partnership-building and brokering
-
Government-led management and monitoring of TC resources
-
Decreasing marginal returns – address duplication and overlap
-
Integrate TC and capacity support into programmatic approaches
|
|
Conclusions
-
Aid
effectiveness work is linked to NSDP results
-
AER as the
basis for broad, ongoing dialogue
-
Implementation of existing policy frameworks
|
|



