 |
2nd Cambodia
Development
Cooperation Forum |
Agricultural
Productivity & Diversification
Paper for:
2nd Cambodia Development Cooperation Forum
on 4-5 December 2008- CDC, Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Presented by: H.E. Chan
Tong Yves,
Secretary of State, MAFF
and Co-Chairs of TWGAW
|
 |
Contents |
-
General Overview of Agriculture Sector
-
Agricultural Productivity and Diversification
2.1 Policy Framework
2.2 Conceptual Framework
-
Achievement
-
Challenges and Constraints
-
Direction and Recommendation
- Conclusion
|
|
I. General Overview of
Agricultural Sector
|
 |
GDP Growth Rate |
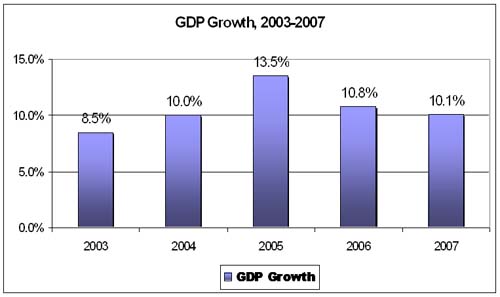
|
 |
GDP by Key sector |
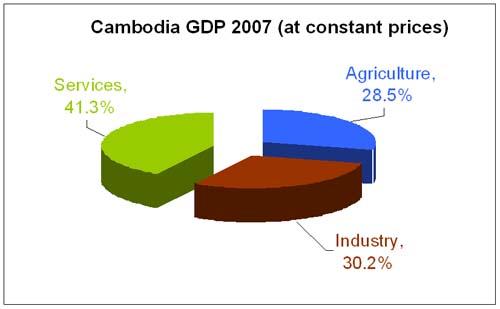
|
 |
Evolution of agricultural sector
in GDP 1998-2007 |
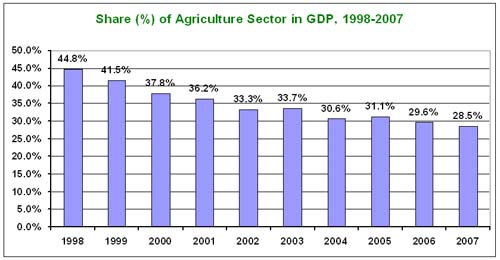
|
 |
Gross
value added of agricultural sector |
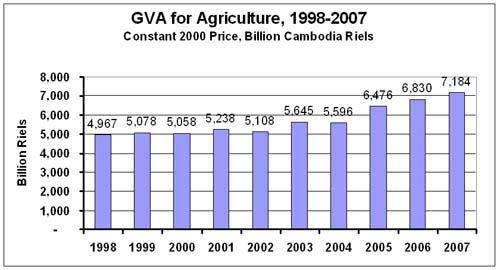
|
 |
Growth
for Agricultural
Sector 1998-2007 |
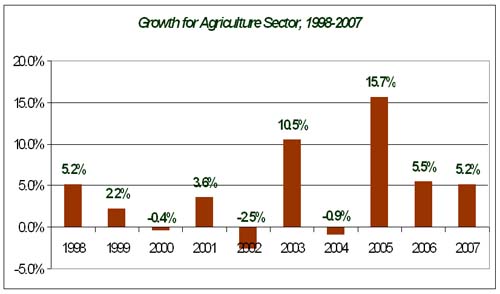
|
 |
Composition of share in agriculture GDP |
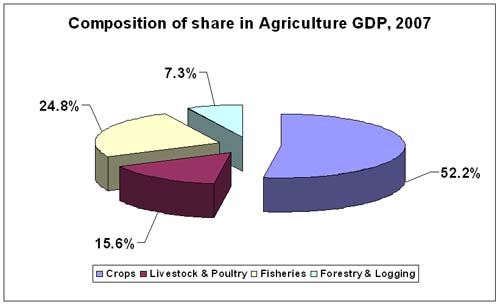
|
 |
Gross
value added by
crops |
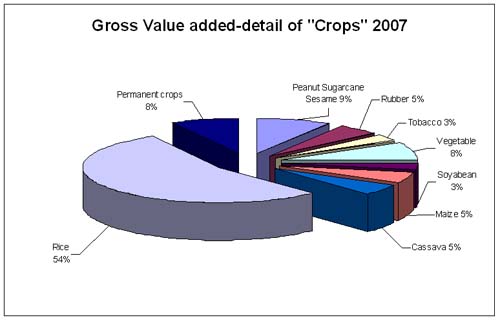
|
|
II. Agricultural Productivity and Diversifications
|
 |
2.1.
Policy frameworks |
|
 |
Rectangular Strategy of RGC |
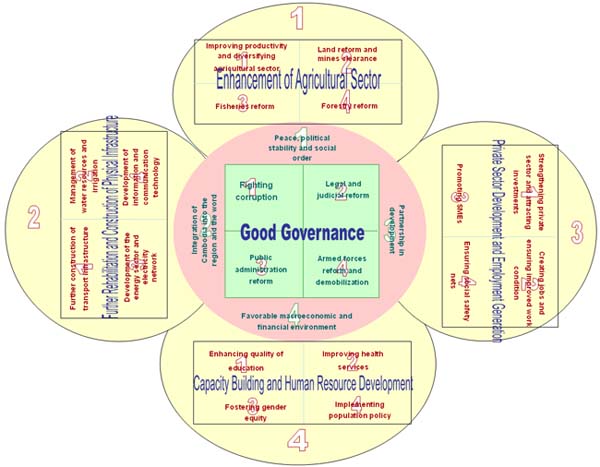
|
 |
2.2.
Conceptual Framework |
-
Agricultural productivity is measured as the return received from the
applied inputs of labor, fertilizer, water etc… and from land.
-
It is expressed in term of land productivity and labor productivity. Labor
productivity is measured as the value of aggregate agricultural output per
hectare of agricultural land: Yield. Labor productivity is measured as value
of aggregate agricultural output per worker.
-
Increase in productivity will lead to increase of value of aggregate
agricultural outputs per hectare of agricultural land and worker.
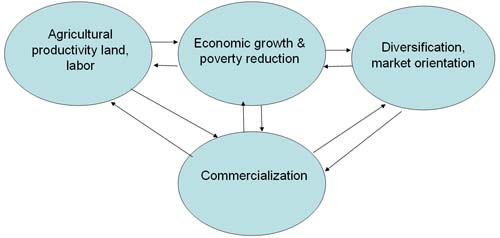
-
Agricultural diversification at the farm household level implies the
addition of other crops and other enterprises.
-
Agricultural diversification at the agriculture sector level is created by
household level specialization as household shift away from traditional
self-sufficiency goals and toward profit and income oriented decision making
with increase responsiveness of farm to market needs.
-
Agricultural diversification and commercialization are inter related as
commercialization lead to greater market orientation of farm production,
progressive substitution of non-traded inputs by purchased inputs and the
gradual decline of integrated farming systems and their replacement by
specialized enterprises for crops, livestock, poultry, and aquaculture
productions etc… and products for bio fuel…
-
Agricultural diversification and commercialization are interrelated as
agricultural commercialization proceeds, the market share of agricultural
output increase.
-
As economy grows, there is a gradual movement out of subsistence food-crops
production to a diversified market oriented production systems.
-
The process of diversification out of staple food crops production is
triggered by:
-
Rapid technological change in agricultural production
-
Improved rural infrastructure
-
Diversification in food demand pattern (diet
diversification).
-
Diversification and commercialization benefit the poor by directly
generating income, employment and increasing agricultural productivity.
-
Agricultural diversification proceeds through:
-
Horticulture revolution: Fruits, vegetables, flowers
-
Livestock and aquaculture revolution
-
Agro-processing and export
-
Bio-Fuel revolutions.
|
 |
III.
Achievement
Progress on Rice Production 2004-2007 |
| Description |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
(%) for 4 years |
| Cultivated
Areas |
2,374,175 |
2,443,530 |
2,541,433 |
2,584,907 |
8% |
| Harvested
Areas |
2,109,050 |
2,414,455 |
2,516,415 |
2,566,954 |
20% |
| Yield (T/ha) |
1.977 |
2.479 |
2.489 |
2.621 |
30% |
| Production (T) |
4,170,284 |
5,986,179 |
6,264,123 |
6,727,138 |
60% |
|
 |
Progress Rice
Production |
-
Harvested area from 2.1 million ha to 2.56 million ha an increase of 8%
-
Production from 4.17 million tones to 6.72 millions tones an increase of
60%.
-
Yield also increased from 1.97t/ha to 2.62 t/ha an increase of 30%.
-
Surplus milled rice increased from 416,118 t to 1,642,040 tons and increase
of 290%
|
 |
Food
Balance |
-
For 2007-08:
-
Production of paddy is 6.72 million tons
-
Surplus of milled rice : 1.64 million tons
-
(or 2.57 million tons of paddy) for export
-
For 2008-09:
-
Production of paddy is 6.778 million tons
-
Surplus of milled rice : 1.803 million tons
-
(or 2.818 million tons of paddy) for export
|
 |
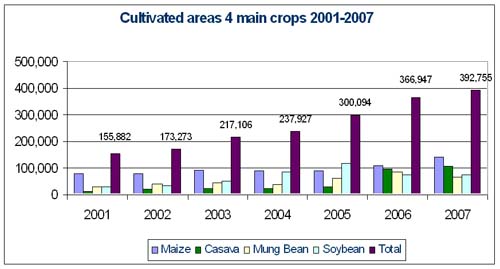
Secondary crops &
industry crops |
-
Secondary crops: Cultivated areas 366,744 ha and production of 3,057,360
tons, including vegetables: 42,360 ha and production: 226,426 tones
-
Industrial Crops: 164,453 ha and 481,160 tons
-
Fruit trees and perennials: 165,000 ha
 |
 |
Rural
Infrastructure |
-
Until 2003: 560,149 ha irrigation capacity representing 24.86% of cultivated
areas
-
In 2008: Irrigation capacity 1,063,581 ha representing 47.20% of cultivated
areas in which wet season 765,335 ha and dry season 298,246 ha
|
 |
Inputs
Use |
-
Fertilizers: Between 175,000 MT and 223,00 MT on rice upland
crops, vegetables, fruit trees average per hectare between 50-70Kg
-
Organic fertilizers and manures: datas not available (need
survey)
-
Pesticides:
-
Liquid: estimated quantity 20,000 liters
-
Powder: estimated quantity 22,630 Kg on rice upland crops,
vegetable, fruit trees. Mechanical controls are currently practised.
|
 |
Rubber
Plantation in 2008 |
-
State owned enterprises: 44,745 ha
-
Private owned and concession : 10,887 ha
-
Smallholder rubber farm : 53,044 ha.
|
 |
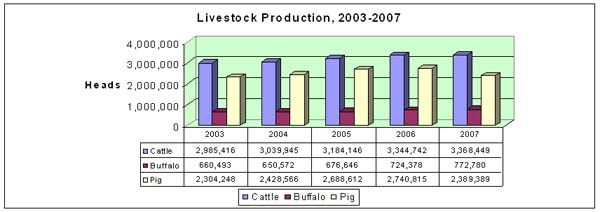
Family
Animal husbandry
2007 |
-
Cattle: 4.141.229 heads an increase 12-16%
-
Pigs: 2.389.389 heads an increase 16%
-
Poultry (chicken & ducks): 15.825.314 head
 |
 |
Semi-
commercial animal farm 2007 |
-
Poultry farms: 902 farms and 1,345,605 heads
-
Pig farm: 287 farms and 60,147 heads
-
Cattle farms: 43 farms and 5,019 heads
|
 |
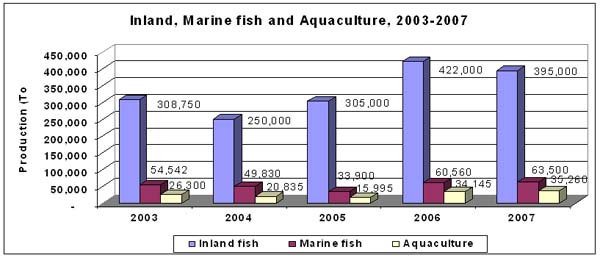
Aquaculture |
-
Fish & shrimp production: 35,260 tons
-
Fish fingerling : 33,778 million heads.
-
Crocodile farms: 128,945 heads
 |
 |
Potential export products |
-
Paddy/Rice (Domestic demand surplus)
-
Seasonal Crops: Maize, Soybean, Mung bean, Sesame, Peanuts, Cassava, Tobacco
-
Perennial Crops: Cashew, Pepper, Rubber…
-
Fish products
-
Cattle/Buffalos.
|
 |
Local
use and export of some Agricultural products |
| Selected Commodities |
Domestic
Consumption
(%) |
Exportation (%) |
| Corn/Maize |
30~40 |
60~70 |
| Soybean |
20~30 |
70~80 |
| Cassava |
20~30 |
70~80 |
| Mung Bean |
35~45 |
55~65 |
| Ground Nut |
40~50 |
50-60 |
| Sesame |
30~40 |
60-70 |
|
 |
Agri-business and Agro-industry in 2007 |
-
Rice mills and cereal mills: 24,227 Units
-
Agro-processing's plants: 142 Units
-
Fishery processing plants: 377 Units
-
Fish processed products: 24,000 tones
-
Fish sauces: 16,500,000 liters
-
Fish product exports: 3,000 tones
-
Dry rubber export: 30,000 tones
-
Cassava: 1,600,000 tones (export and locally processed).
|
 |
IV.
Challenges and Constraints |
-
Inadequate rural infrastructures: Roads, irrigation systems, rural markets…
-
Limited technological changes at community level as well as farmers and
producers, agricultural research and extension are still inadequate.
-
Limited access to credits and micro-finances in the rural areas.
-
Limited investment capacity or interest in investing in agriculture.
-
Low soil fertility in some areas
-
Variable climatic condition and water resources
-
Limited access to agriculture inputs: fertilizers
-
(chemical organic), pesticides, machineries, improved seeds…
-
Weak agri-business and agro-enterprises.
-
Export constraints due to technical barriers (Quality standard, quality
control, quality certifications)
-
Regional disparities
-
Landless among poor farmers.
|
 |
V.
Direction and Recommendations |
-
Investment in irrigation and water control (Public & private)
-
Investment in rural markets, transportations and communication
infrastructure to facilitate the integration of markets and reduction in
regional disparities
-
Improvement in agricultural research and extension. For extension adopt a
policy of grass-root extension systems
-
Development of rural financial markets
-
Investment in productivity and conservation- enhancing technology by
improving soil fertility, using best agricultural practices, efficient and
effective use of agricultural inputs and water, best practices in
post-harvest technology, ect…
-
Encourage private sector to invest in agricultural research and extension,
irrigation, agri-business, and agro-enterprise, livestock and aquaculture
development
-
Improve access to world market for agricultural products including livestock
(poultry if possible), fish products etc…
-
Establishment of agricultural development communities
-
Secure right to land for farmers
-
Invest in education for better transfer of technology to improve labor
productivity and facilitate transition from subsistence food production to
commercial agriculture through diversifications
-
Improve agricultural statistics
-
Start agricultural census.
|
 |
Conclusions |
-
Support increasing food production and ensure food security in the country.
-
Create job opportunity and increase incomes in rural areas.
-
Increase export of agri-products.
-
Increase contribution to processing plant and producing bio-fuels.
-
Based on increasing demand of rice, maize, beans, cassava rubber products in
local and world market and bio-fuel production, agricultural productivity
and diversifications will be developed in Cambodia.
-
Thanks to all EDPs for their great contribution to agricultural sector
development for economic growth and poverty reduction. For Efforts are
needed to improve agricultural performances with regards to productivity and
diversification
|
|







